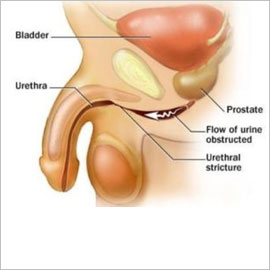
Urethral Stricture refers to any narrowing of the urethra for any reason whether or not it actually impacts the flow of urine out of the bladder. Any inflammation of urethra can result in scarring, which then can lead to a stricture or a narrowing of the urethra. Trauma, infection, tumors, surgeries, or any other cause of scarring may lead to urethral narrowing or stricture. Mechanical narrowing of the urethra without scar formation (developmental causes or prostate enlargement) can also cause urethral stricture. Urethral stricture is significantly more common in men and boys compared to women and girls. This condition is considered rare infemales.
Causes Of Urethral Stricture
Trauma from injury or accidents with damage to the urethra or bladder (for example, falling on a frame of a bicycle between the legs, or a car accident)
Pelvic injury or trauma
Previous procedures involving the urethra (urinary catheters, surgeries, cystoscopy)
Previous prostate surgery (TURP or transurethral resection of the prostate)
Prostate enlargement
Cancer of the urethra (rare)
Infections of the urethra (sexually transmitted diseases or STDs, urethritis, gonorrhea, chlamydia)
Prostate infection or inflammation (prostatitis)
Previous hypospadias surgery (a congenital birth defect in which the opening of the urethra is on the underside of the penis instead of the tip)
Congenital malformations of the urethra, which rarely can cause urethral stricture in children
Signs and symptoms of Urethral Stricture
Difficulty starting urine flow
Painful urination (dysuria)
Urinary tract infection (UTI)
Urinary retention
Incomplete emptying of bladder
Decreased urine stream
Dribbling of urine
Spraying or double streaming urine
Blood in the urine (hematuria)
Blood in the semen
Urinary incontinence
Pelvic pain
Discharge from the urethra
Investigation for Stricture Urethra
Cystoscopy: Cystoscopy is endoscopy of the urinary bladder via the urethra. It is carried out with a cystoscope. The cystoscope is inserted into your urethra and slowly advanced into the bladder.
Urethrography: A retrograde urethrogram is a routine radiologic procedure used to image the integrity of the urethra. Hence a retrograde urethrogram is essential for diagnosis of urethral injury, or urethral stricture.
Uroflowmetry: Uroflowmetry is a diagnostic test that is administered to check for abnormalities in the amount or flow rate of a patients urine. The procedure is straightforward and painless, and simply involves urinating into a funnel device attached to an electronic meter.
Treatment Of Stricture Urethra
Urethral dilation.
Internal and Laser Urethrotomy.
Holmium laser urethrotomy.
Urethroplasty.